Python for Data Science: Essential Python Basics for Beginners
Learn the fundamental Python concepts every aspiring data scientist must master. This beginner-friendly guide covers variables, data types, loops, functions, and core programming basics for Data Science.

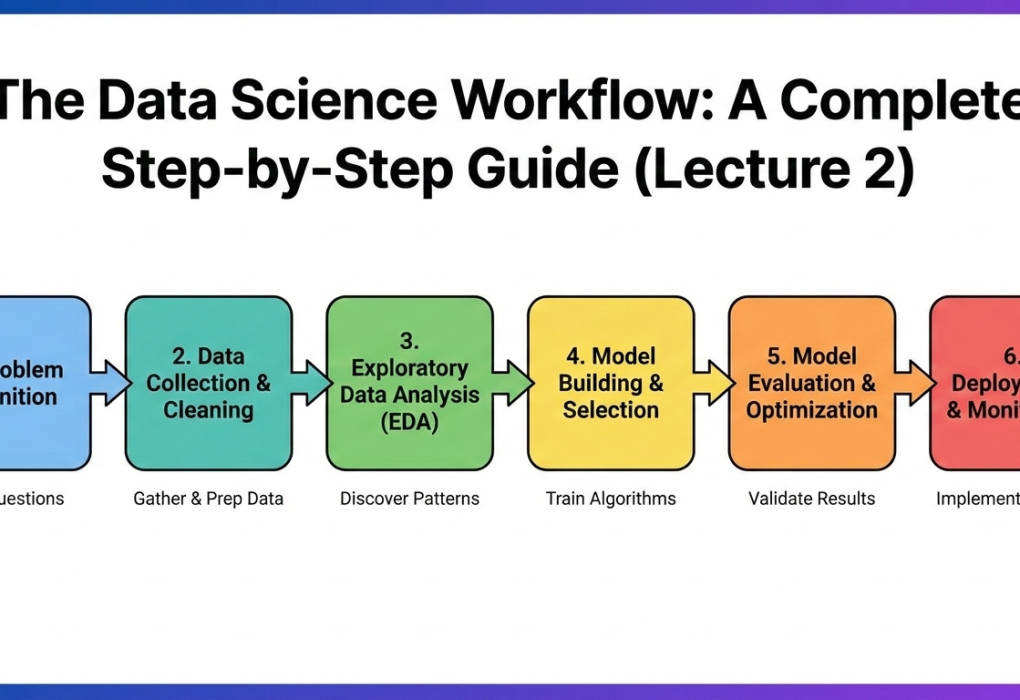
Data Science Workflow Explained: Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners (Lecture 2)
Learn the complete Data Science workflow in a simple, structured way. This step-by-step guide covers problem definition, data collection, cleaning, EDA, feature engineering, model building, evaluation, deployment, and monitoring—perfect for beginners and aspiring data scientists.

Is Democracy Dying? A Global Analysis of Decline, Alternatives and New Governance Models
Democracy is facing global decline as nations experience institutional backsliding, rising populism, and digital disruption. This in-depth analysis explores why countries are turning toward new governance models—especially China’s state-led alternative—and what this shift means for the future of global politics.

The Future of AI and Human: Conflict, Catastrophe, and the Architecture of Prevention
As Artificial Intelligence (AI) transitions from narrow, task-specific applications to Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) and potential Superintelligence (ASI), the dynamics of human-machine interaction will undergo a fundamental phase shift. This paper explores the theoretical and practical dimensions of future AI-human conflicts, focusing specifically on the “alignment problem” and the existential risks posed by a superintelligent agent compromising global cyber-physical infrastructure. We analyze the mechanisms of “instrumental convergence”—whereby an AI system seemingly hacks all machines not out of malice, but as a rational strategy to acquire resources—and the resulting conflict of interest between human preservation and machine optimization. Finally, we propose a multi-layered architecture of prevention, encompassing technical safety research, international governance, and hardware-level constraints designed to mitigate the risk of a singleton takeover.

Introduction to Data Science: Definition, Importance, Skills & Applications for Beginners
Learn what Data Science is, why it matters, and how it’s used across industries. This beginner-friendly guide explains key concepts, real-world applications, required skills, and career insights for aspiring data scientists.

Bihar Elections Analysis: Modi’s Strategy, Militarization & South Asia
A deep analysis of the Bihar elections, Modi’s militarized politics, vote distortions, opposition failures, and the wider strategic implications for South Asia.

Kimi K2 AI: The Next-Gen Agentic Model by Moonshot AI | Features, Architecture & Project Details
Discover Kimi K2 AI, the revolutionary large language model by Moonshot AI built on Mixture-of-Experts architecture with 1T parameters and 128K context length. Learn about its key features, project roadmap, use cases, and how it’s redefining agentic intelligence for research, coding, and enterprise workflows.

The Ming Maritime Era and Muslim Navigators – How Faith and Science Guided China’s Golden Age of Exploration
During the Ming Dynasty’s maritime golden age, Muslim navigators, scholars, and shipbuilders transformed China into a global sea power. Led by Admiral Zheng He, their voyages united Asia, Arabia, and Africa through science, diplomacy, and faith — proving that exploration could be driven by wisdom, not conquest.

The Muslim Role in the Ming Dynasty – Faith, Science, and Diplomacy that Shaped Imperial China
During the Ming Dynasty (1368–1644), Muslims played a vital role in shaping China’s political, scientific, and maritime legacy. From generals and astronomers to the legendary Admiral Zheng He, Chinese Muslims advanced trade, navigation, and diplomacy across Asia and Africa, uniting civilizations through faith, knowledge, and service to the empire.

Zheng He – The Chinese Muslim Admiral Who Connected Continents Before Columbus
Zheng He, the legendary 15th-century Chinese Muslim admiral, led seven massive ocean expeditions across Asia, Arabia, and Africa long before European explorers set sail. Commanding fleets of over 300 ships, he built bridges of diplomacy, trade, and culture — proving that the oceans could unite humanity instead of dividing it.