Analyzing the Correlation Between the Rise of the LGBTQ+ Community and Declining Birth Rates in European Countries
1. Introduction
1.1. Overview of Birth Rate Trends in Europe
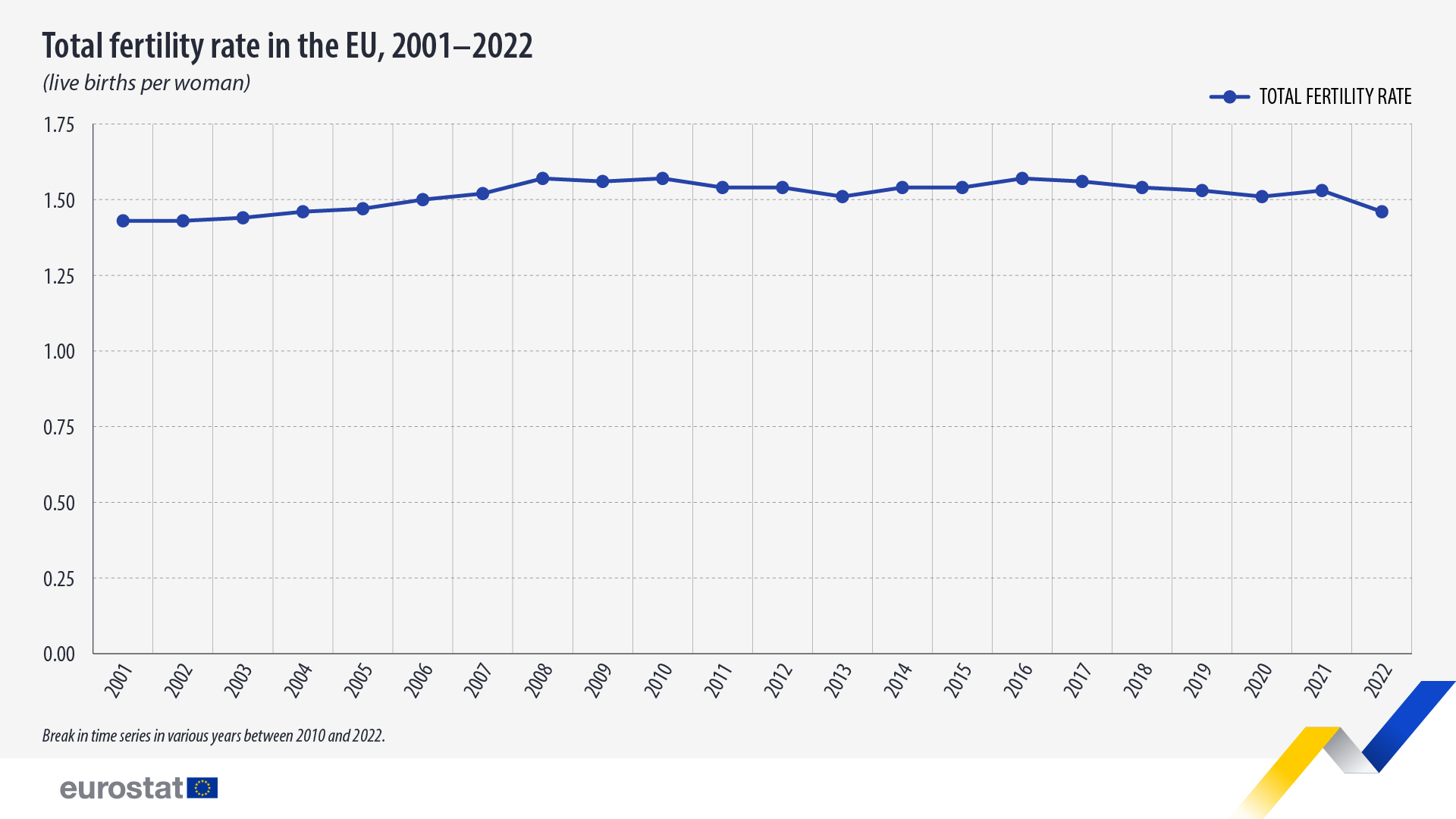
The birth rate in Europe has been on a consistent decline for several decades. According to Eurostat, the average total fertility rate (TFR) in the European Union (EU) has decreased from around 2.1 children per woman in the early 1960s to approximately 1.5 in recent years. This significant drop has raised concerns about potential demographic and economic consequences, such as an aging population and a shrinking labor force. As European countries grapple with these challenges, understanding the factors contributing to low birth rates has become increasingly critical.
1.2. Introduction to LGBTQ+ Community Growth
The visibility and social acceptance of the LGBTQ+ community have seen substantial growth across Europe. Many countries have enacted progressive legislation supporting LGBTQ+ rights, including the legalization of same-sex marriage and the introduction of anti-discrimination laws. This shift has resulted in a broader acceptance of diverse family structures and has raised questions about how these changes might impact demographic trends.
1.3. Purpose of Analysis
This analysis seeks to explore the potential correlation between the rise of the LGBTQ+ community and declining birth rates in European countries. By examining various factors, including legal, economic, and societal influences, this paper aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how these dynamics interact and impact demographic trends.
2. Demographic Trends in Europe
2.1. Historical Birth Rate Trends
Europe’s post-World War II era was marked by a significant baby boom, driven by economic recovery and increased family stability. However, starting in the 1960s, birth rates began to decline steadily. This trend has been attributed to various factors, including changing societal norms, increased educational and employment opportunities for women, and economic uncertainties. The shift from traditional family structures to more individualistic and career-focused lifestyles has contributed to the decrease in birth rates.
2.2. Current Birth Rate Statistics
Recent statistics highlight the severity of the decline in birth rates. As of 2023, Italy’s birth rate stands at approximately 1.2 children per woman, while Germany’s rate is around 1.4. Other European countries, such as Spain and Greece, also exhibit similarly low birth rates. These figures are significantly below the replacement level of 2.1 children per woman, which is necessary to maintain a stable population size. The low birth rates across Europe are indicative of broader demographic and societal changes.
2.3. Projections for Future Birth Rates
Projections from the United Nations suggest that birth rates in Europe will continue to remain low. Factors such as economic instability, evolving societal values, and changes in family structures are expected to sustain these trends. The anticipated continuation of low birth rates may further exacerbate challenges related to population aging and economic growth, necessitating policy interventions to address these issues.
3. LGBTQ+ Rights and Visibility
3.1. Evolution of LGBTQ+ Rights in Europe
The evolution of LGBTQ+ rights in Europe has been marked by significant legal and societal changes. The Netherlands was the first country to legalize same-sex marriage in 2001, followed by Belgium, Spain, and other European nations. The introduction of anti-discrimination laws and recognition of same-sex partnerships have contributed to increased social acceptance and integration of LGBTQ+ individuals. This progressive shift has had a notable impact on family structures and societal norms.
3.2. Increased Visibility and Social Acceptance
The visibility and social acceptance of LGBTQ+ individuals have grown substantially in recent years. According to Pew Research Center, support for LGBTQ+ rights has increased across Europe, with many countries demonstrating high levels of acceptance for same-sex relationships and LGBTQ+ families. This increase in visibility and acceptance reflects broader societal changes and challenges traditional views on family composition.
3.3. Impact on Family Structures
The rise in LGBTQ+ rights has led to the emergence of diverse family structures, including same-sex couples and families formed through adoption and surrogacy. Research from the American Psychological Association indicates that children raised in same-sex households experience similar developmental outcomes as those raised in heterosexual households. This evidence supports the notion that family composition is evolving, and traditional definitions of family are being redefined in contemporary society.
4. Marriage and Family Formation Among LGBTQ+ Individuals
4.1. Legalization of Same-Sex Marriage
The legalization of same-sex marriage has significantly influenced family formation among LGBTQ+ individuals. Countries such as the UK, France, and Germany have seen a rise in same-sex marriages, allowing LGBTQ+ couples to formalize their relationships legally. This legal recognition has provided greater stability and societal acceptance for LGBTQ+ families, affecting their family planning decisions and contributing to demographic changes.
4.2. Adoption and Parenting Rights
Adoption and parenting rights for LGBTQ+ individuals have expanded considerably in many European countries. For example, Sweden and Portugal have granted same-sex couples equal adoption rights, enabling them to build families through legal means. However, adoption rights remain restricted in some countries, limiting family formation opportunities for LGBTQ+ couples. This disparity in adoption rights influences family structures and overall birth rates.
4.3. Changes in Family Dynamics
The inclusion of LGBTQ+ individuals in family structures has led to shifts in traditional family dynamics. Same-sex couples often adopt alternative family-building methods, such as surrogacy and adoption, which can influence demographic patterns. The diversification of family structures reflects broader societal changes and contributes to the evolving landscape of family formation.
5. Economic Factors
5.1. Economic Impact of LGBTQ+ Rights
The economic impact of LGBTQ+ rights includes changes in household income and spending patterns. Studies by the Williams Institute reveal that LGBTQ+ individuals often experience higher disposable incomes due to factors such as delayed family formation and dual-income households. This economic shift influences consumption patterns and overall economic activity, potentially affecting birth rates.
5.2. Influence on Household Income and Spending
LGBTQ+ individuals and couples may experience different financial dynamics compared to traditional families. Research from the European Commission shows that same-sex couples often have higher educational attainment and career aspirations, leading to increased household income and spending capacity. These financial dynamics can influence family planning decisions and impact birth rates.
5.3. Economic Implications for Birth Rates
Economic factors play a crucial role in birth rate trends. High living costs, economic uncertainty, and career-focused lifestyles contribute to delayed family formation and smaller family sizes. The economic stability of LGBTQ+ individuals may influence their family planning decisions and impact overall birth rates, reflecting broader economic and societal trends.
6. Societal Attitudes and Cultural Shifts
6.1. Changing Attitudes Towards LGBTQ+ Families
Societal attitudes towards LGBTQ+ families have evolved significantly. Public opinion surveys, such as those conducted by the European Social Survey, indicate increasing acceptance of diverse family structures. This cultural shift influences how LGBTQ+ families are perceived and supported, contributing to changes in family planning and birth rates.
6.2. Cultural Influences on Family Formation
Cultural values and societal norms shape family formation practices. The growing acceptance of LGBTQ+ families reflects broader cultural changes, including shifts in attitudes towards marriage, parenting, and family structures. These cultural influences contribute to changing birth rates and family dynamics, reflecting evolving societal values.
6.3. Impact on Birth Rate Trends
Cultural and societal shifts impact birth rate trends by influencing family planning decisions and societal expectations. As attitudes towards LGBTQ+ families become more inclusive, traditional family structures and birth rates may undergo further changes. This evolution reflects broader trends in societal values and family composition.
7. Healthcare and Reproductive Technologies
7.1. Access to Reproductive Health Services for LGBTQ+ Individuals
Access to reproductive health services for LGBTQ+ individuals has improved significantly in recent years. Many European countries now offer fertility treatments, surrogacy options, and other reproductive health services to LGBTQ+ individuals and couples. This increased access supports family formation and influences demographic trends.
7.2. Impact of Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) on Birth Rates
Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART), such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) and artificial insemination, have played a role in family formation for LGBTQ+ individuals. Research shows that ART can influence birth rates by providing alternative pathways to parenthood. The availability and use of ART contribute to changes in family structures and demographic patterns.
7.3. Differences in Reproductive Health Access Across Europe
Access to reproductive health services varies across Europe. While some countries offer comprehensive support for LGBTQ+ individuals, others have more restrictive policies. These differences in access impact family formation and birth rates, reflecting variations in societal attitudes and healthcare infrastructure.
8. Educational Attainment and Career Goals
8.1. Influence of Education on Family Planning
Educational attainment plays a significant role in family planning decisions. Higher levels of education are often associated with delayed family formation and smaller family sizes. This trend is observed among LGBTQ+ individuals and heterosexual couples, influencing overall birth rates.
8.2. Career Aspirations and Their Effect on Birth Rates
Career aspirations and professional goals impact family planning decisions. Individuals who prioritize career development may delay or forgo having children, contributing to declining birth rates. This trend is evident among both LGBTQ+ individuals and heterosexual couples, reflecting broader societal shifts in work-life balance.
8.3. LGBTQ+ Educational and Career Trends
LGBTQ+ individuals often experience distinct educational and career trends compared to their heterosexual counterparts. Research indicates that LGBTQ+ individuals may have higher educational attainment and career aspirations, influencing their family planning decisions and contributing to demographic changes.

9. Public Opinion and Media Representation
9.1. Influence of Media on Perceptions of LGBTQ+ Families
Media representation plays a crucial role in shaping perceptions of LGBTQ+ families
. Positive and inclusive media portrayals can contribute to greater acceptance and support for diverse family structures. This media influence impacts public opinion and policy decisions related to family formation and birth rates.
9.2. Shifts in Public Opinion Regarding Family Structures
Public opinion on family structures has evolved with increased visibility and acceptance of LGBTQ+ families. Surveys and opinion polls reflect changing attitudes towards diverse family arrangements, impacting societal norms and birth rates. Understanding these shifts provides insights into broader demographic trends.
9.3. Media Coverage of LGBTQ+ Issues and Its Effects
Media coverage of LGBTQ+ issues influences public perceptions and policy decisions. Inclusive and supportive media coverage can enhance acceptance and impact family formation. Analyzing media trends offers valuable insights into the broader societal impact of LGBTQ+ visibility and rights.
10. Conclusion
10.1. Summary of Key Findings
The analysis reveals a complex relationship between the rise of the LGBTQ+ community and declining birth rates in Europe. Key findings include the influence of legal, economic, and societal factors on family formation and birth rates. Cultural shifts, media representation, and evolving family structures collectively contribute to demographic changes.
10.2. Implications for Future Research
Future research should explore the long-term implications of LGBTQ+ rights and visibility on demographic trends. Studies could examine how evolving family structures impact economic and social policies, offering insights into potential solutions for addressing declining birth rates.
10.3. Potential Policy Recommendations
Policy recommendations include promoting inclusive family policies, enhancing support for diverse family structures, and addressing economic factors affecting birth rates. By fostering a supportive environment for all families, policymakers can work towards reversing declining birth rates and ensuring a stable demographic future.